How Does a Battery Electric Vehicle Differ from a Plug-in Hybrid?
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) use a combination of battery power and a gasoline engine to extend range. Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) are fully electric, using battery power only. Currently, some models can drive up to 300 miles on a single charge.
BEV Overview
For drivers who want to achieve zero tailpipe emissions and have access to charging opportunities. BEVs are eligible for the Oregon Clean Vehicle Rebate Program.
BEVs use a larger battery to run one or more electric motors and can be plugged in at home, work or public charging stations. As a benefit, BEVs require limited maintenance—you will never need oil changes or new spark plugs again.
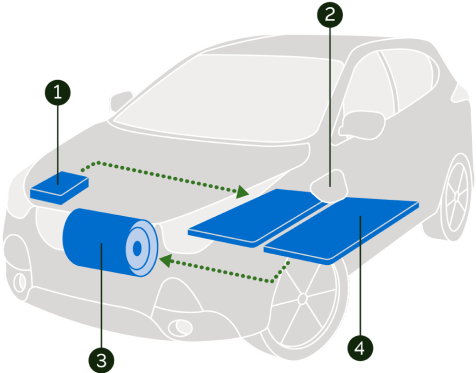
- Onboard Charger – Converts incoming AC electricity to DC power for charging the battery.
- Charge Port – Enables the car to be plugged in to an external power source to charge the battery.
- Electric Motor – Powered from the battery, the electric motor propels the car at all times.
- Battery – Typically positioned below the seats for better weight distribution, these batteries can be as large as 100kWh and power the electric motor.
PHEV Overview
For drivers who want an electric mode, but still need the option of gas to allow for longer distances. PHEVs are eligible for the Oregon Clean Vehicle Rebate Program.
PHEVs offer both gas-only and electric-only driving—even at high speeds. With smaller batteries than BEVs, they charge by plugging in and using regenerative braking.
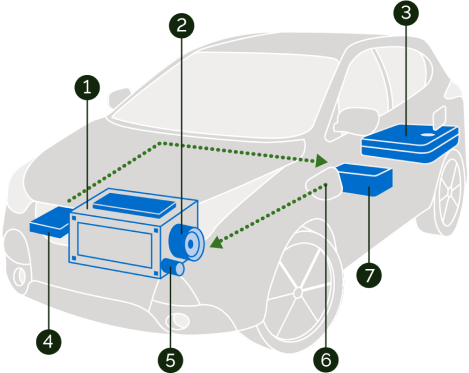
- Engine – Assists electric motor when driving at high speeds, and powers the vehicle when the battery is depleted.
- Electric Motor – Powered from the battery, the electric motor propels the vehicle up to high speeds.
- Gas Tank – Smaller gas tank than conventional cars.
- Onboard Charger – Converts incoming AC electricity to DC power for charging the battery.
- Electric Generator – Captures energy from regenerative braking and transfers to battery.
- Charge Port – Enables the vehicle to be plugged in to an external power source to charge battery.
- Battery – Stores typically between 8-16 kWh of electricity to power the electric motor.
